Gallbladder
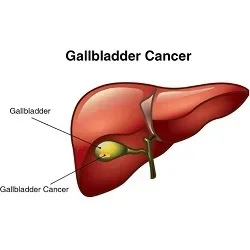
Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer is often difficult to detect early because its symptoms are not specific and can be mistaken for other, more common conditions like gallstones or gallbladder inflammation. When symptoms do appear, they can be a sign that the disease has progressed.
Symptoms
* Abdominal Pain: Persistent and severe pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, which may spread to the back.
* Jaundice: A yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. This happens when a tumor blocks the bile ducts, causing a buildup of bilirubin in the body.
* Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without any change in diet or exercise.
* Nausea and Vomiting: A feeling of sickness and throwing up.
* Bloating: A feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen, even after a small meal.
* Dark Urine and Light-Colored Stools: The color change is due to the same bile duct blockage that causes jaundice.
Gallbladder cancer is often difficult to detect early because its symptoms are not specific and can be mistaken for other, more common conditions like gallstones or gallbladder inflammation. When symptoms do appear, they can be a sign that the disease has progressed.
Symptoms
* Abdominal Pain: Persistent and severe pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, which may spread to the back.
* Jaundice: A yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. This happens when a tumor blocks the bile ducts, causing a buildup of bilirubin in the body.
* Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without any change in diet or exercise.
* Nausea and Vomiting: A feeling of sickness and throwing up.
* Bloating: A feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen, even after a small meal.
* Dark Urine and Light-Colored Stools: The color change is due to the same bile duct blockage that causes jaundice.
Main Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause is not fully understood, a number of factors are known to increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
Gallstones (Cholelithiasis): This is the most significant risk factor. A long history of gallstones, especially large ones, is strongly linked to gallbladder cancer. The chronic irritation and inflammation caused by gallstones are believed to play a role in the development of cancer.
Chronic Gallbladder Inflammation (Chronic Cholecystitis): Long-term inflammation of the gallbladder, often due to gallstones, is a major risk factor.
Porcelain Gallbladder: This is a rare condition where the gallbladder wall becomes calcified. It is often a result of chronic inflammation and is associated with a higher risk of cancer.
Age and Gender: Gallbladder cancer is more common in older adults and is significantly more prevalent in women than in men.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of both gallstones and gallbladder cancer.
Side effects of steroid or Alopathic medicines
Genetic Family history
While the exact cause is not fully understood, a number of factors are known to increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
Gallstones (Cholelithiasis): This is the most significant risk factor. A long history of gallstones, especially large ones, is strongly linked to gallbladder cancer. The chronic irritation and inflammation caused by gallstones are believed to play a role in the development of cancer.
Chronic Gallbladder Inflammation (Chronic Cholecystitis): Long-term inflammation of the gallbladder, often due to gallstones, is a major risk factor.
Porcelain Gallbladder: This is a rare condition where the gallbladder wall becomes calcified. It is often a result of chronic inflammation and is associated with a higher risk of cancer.
Age and Gender: Gallbladder cancer is more common in older adults and is significantly more prevalent in women than in men.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of both gallstones and gallbladder cancer.
Side effects of steroid or Alopathic medicines
Genetic Family history
पित्ताशय का कैंसर
पित्ताशय का कैंसर अक्सर शुरुआती चरणों में पता लगाना मुश्किल होता है क्योंकि इसके लक्षण विशिष्ट नहीं होते हैं और पित्त की पथरी या पित्ताशय की सूजन जैसी अन्य, अधिक सामान्य स्थितियों के लिए गलत समझे जा सकते हैं। जब लक्षण दिखाई देते हैं, तो यह इस बात का संकेत हो सकता है कि बीमारी बढ़ गई है।
लक्षण :-
पेट में दर्द : पेट के ऊपरी दाहिने हिस्से में लगातार और तेज दर्द, जो पीठ तक भी फैल सकता है।
पीलिया (Jaundice): त्वचा और आंखों के सफेद हिस्से का पीला पड़ना। यह तब होता है जब ट्यूमर पित्त नलिकाओं को अवरुद्ध कर देता है, जिससे शरीर में बिलीरुबिन का जमाव हो जाता है।
बिना कारण वजन घटना: बिना किसी आहार या व्यायाम में बदलाव के अचानक वजन कम होना।
मतली और उल्टी: बीमार महसूस करना और उल्टी करना।
पेट में सूजन: कम भोजन के बाद भी पेट में भरापन या सूजन महसूस होना।
गहरा पेशाब और हल्के रंग का मल: रंग में यह बदलाव उसी पित्त नली के अवरोध के कारण होता है जिससे पीलिया होता है।
मुख्य कारण और जोखिम कारक
हालांकि सटीक कारण पूरी तरह से ज्ञात नहीं है, लेकिन कई कारक पित्ताशय के कैंसर के विकसित होने के जोखिम को बढ़ाते हैं।
पित्त की पथरी (Gallstones): यह सबसे महत्वपूर्ण जोखिम कारक है। पित्त की पथरी का एक लंबा इतिहास, विशेष रूप से बड़ी पथरी, पित्ताशय के कैंसर से दृढ़ता से जुड़ा हुआ है। माना जाता है कि पित्त की पथरी के कारण होने वाली पुरानी जलन और सूजन कैंसर के विकास में भूमिक निभाती है।
पित्ताशय की पुरानी सूजन (Chronic Gallbladder Inflammation): पित्ताशय की लंबे समय तक सूजन, जो अक्सर पित्त की पथरी के कारण होती है, एक प्रमुख जोखिम कारक है।
पोर्सिलेन पित्ताशय (Porcelain Gallbladder): यह एक दुर्लभ स्थिति है जिसमें पित्ताशय की दीवार कैल्सीफाइड हो जाती है। यह अक्सर पुरानी सूजन का परिणाम होता है और कैंसर के अधिक जोखिम से जुड़ा होता है।
उम्र और लिंग: पित्ताशय का कैंसर वृद्ध वयस्कों में अधिक आम है और पुरुषों की तुलना में महिलाओं में काफी अधिक प्रचलित है।
मोटापा (Obesity): अधिक वजन या मोटापे से पित्त की पथरी और पित्ताशय के कैंसर दोनों का खतरा बढ़ जाता है।
स्टेरॉयड या एलोपैथिक दवा के दुष्प्रभाव
आनुवंशिक पारिवारिक इतिहास
पित्ताशय का कैंसर अक्सर शुरुआती चरणों में पता लगाना मुश्किल होता है क्योंकि इसके लक्षण विशिष्ट नहीं होते हैं और पित्त की पथरी या पित्ताशय की सूजन जैसी अन्य, अधिक सामान्य स्थितियों के लिए गलत समझे जा सकते हैं। जब लक्षण दिखाई देते हैं, तो यह इस बात का संकेत हो सकता है कि बीमारी बढ़ गई है।
लक्षण :-
पेट में दर्द : पेट के ऊपरी दाहिने हिस्से में लगातार और तेज दर्द, जो पीठ तक भी फैल सकता है।
पीलिया (Jaundice): त्वचा और आंखों के सफेद हिस्से का पीला पड़ना। यह तब होता है जब ट्यूमर पित्त नलिकाओं को अवरुद्ध कर देता है, जिससे शरीर में बिलीरुबिन का जमाव हो जाता है।
बिना कारण वजन घटना: बिना किसी आहार या व्यायाम में बदलाव के अचानक वजन कम होना।
मतली और उल्टी: बीमार महसूस करना और उल्टी करना।
पेट में सूजन: कम भोजन के बाद भी पेट में भरापन या सूजन महसूस होना।
गहरा पेशाब और हल्के रंग का मल: रंग में यह बदलाव उसी पित्त नली के अवरोध के कारण होता है जिससे पीलिया होता है।
मुख्य कारण और जोखिम कारक
हालांकि सटीक कारण पूरी तरह से ज्ञात नहीं है, लेकिन कई कारक पित्ताशय के कैंसर के विकसित होने के जोखिम को बढ़ाते हैं।
पित्त की पथरी (Gallstones): यह सबसे महत्वपूर्ण जोखिम कारक है। पित्त की पथरी का एक लंबा इतिहास, विशेष रूप से बड़ी पथरी, पित्ताशय के कैंसर से दृढ़ता से जुड़ा हुआ है। माना जाता है कि पित्त की पथरी के कारण होने वाली पुरानी जलन और सूजन कैंसर के विकास में भूमिक निभाती है।
पित्ताशय की पुरानी सूजन (Chronic Gallbladder Inflammation): पित्ताशय की लंबे समय तक सूजन, जो अक्सर पित्त की पथरी के कारण होती है, एक प्रमुख जोखिम कारक है।
पोर्सिलेन पित्ताशय (Porcelain Gallbladder): यह एक दुर्लभ स्थिति है जिसमें पित्ताशय की दीवार कैल्सीफाइड हो जाती है। यह अक्सर पुरानी सूजन का परिणाम होता है और कैंसर के अधिक जोखिम से जुड़ा होता है।
उम्र और लिंग: पित्ताशय का कैंसर वृद्ध वयस्कों में अधिक आम है और पुरुषों की तुलना में महिलाओं में काफी अधिक प्रचलित है।
मोटापा (Obesity): अधिक वजन या मोटापे से पित्त की पथरी और पित्ताशय के कैंसर दोनों का खतरा बढ़ जाता है।
स्टेरॉयड या एलोपैथिक दवा के दुष्प्रभाव
आनुवंशिक पारिवारिक इतिहास

